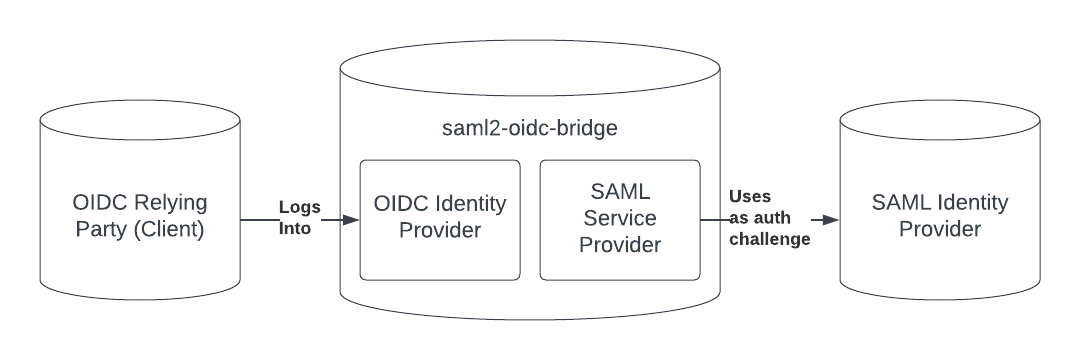
saml2-oidc-bridge
A server the allows OIDC applications to work with SAML identity providers.
Setup
See the setup tutorial for a more in-depth description of setting up the server.
Step 1: Download the library
npm install -g saml2-oidc-bridgeStep 2: Proxy Configuration
If you plan to deploy with nginx, follow the configuration listed below. This guide does not detail setting up SSL, but it is suggested to do so as most SAML providers will not work without SSL.
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3000;
proxy_redirect off;
Step 3: Generate Keys
Four keys must be generated for this project. They can all be saved to separate files. This solution uses OpenSSL, so be sure that is installed first.
SAML Client Public and Private Key
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -new -nodes -x509 -days 3650 -keyout saml-client-key.pem -out saml-client-cert.pem
This should generate two files. saml-client-key.pem (the private key) and saml-client-cert.pem (the public key).
SAML IDP Public Keys
Each SAML IDP must have a public key. To find the public key for a particular SAML IDP, look for the <ds:X509Certificate> tag. We'll call this file saml-idp-key.crt.
OIDC JWKS
JSON Web Key Sets can be here. Once you generate the key, select the center value labeled "Public and Private Keypair Set". We'll call this file oidc-jwks.json
Step 4: Deploy Redis
Deploy a redis server that is accessible from your machine.
Step 5: Configuration
Create a json file and fill it with a configuration like the one below. We'll call it config.json.
{
"baseUrl": "https://saml2-oidc-bridge.com",
"port": "3000",
"saml": {
"privateKey": "./saml-client-key.pem",
"cert": "./saml-client-cert.pem",
"idps": [
{
"name": "example-saml-idp",
"displayName": "Example SAML IDP",
"sso_login_url": "https://example-saml-idp.com/login",
"sso_logout_url": "https://example-saml-idp.com/logout",
"certificates": "saml-idp-key.crt"
},
]
},
"oidc": {
"clients": [
{
"client_id": "some-client-id",
"client_secret": "client-secret",
"redirect_uris": [
"https://oidcdebugger.com/debug"
],
"allowedOrigins": [
"https://oidcdebugger.com"
],
"token_endpoint_auth_method": "none"
}
],
"cookieKeys": ["secret", "keys"],
"jwks": "./oidc-jwks.json"
},
"redis": {
"port": 6379,
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"prefix": "oidc:"
}
}-
baseUrl: The URL you will deploy the bridge at -
port: The port the server should listen at -
saml: SAML configurations. The saml2-oidc-bridge is treated as a SAML client for IDPs-
saml.privateKey: The private key generated in the previous step -
saml.cert: The cert (public key) generated in the previous step -
idps: A list of SAML IDPs this bridge should serve-
saml.idps[*].name: A url-safe name for the idp. This will eventually be used to tell the saml2-oidc-bridge which idp it should try to login to. -
saml.idps[*].displayName: A plain english name for the IDP. This will be used in a UI that lets the user select the IDP they want to login to. -
saml.idps[*].sso_login_url: The login URL for the IDP. This can be found in the IDP metadata in thelocationfield for theSingleSignOnServicetag with a binding ofurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect. (<SingleSignOnService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect" Location="https://example-saml-idp.com/login" />) -
saml.idps[*].sso_logout_url: The logout URL for the IDP. This can be found in the IDP metadata in thelocationfield for theSingleLogoutServicetag with a binding ofurn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect. (<SingleLogoutService Binding="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect" Location="https://example-saml-idp.com/logout" />) -
saml.idps[*].certificates: A list of certificates retrieved for the IDP metadata in the previous step.
-
-
-
oidc: OIDC configurations. The saml2-oidc-bridge is treated as an IDP for OIDC clients-
oidc.clients: A list of all the clients that can authenticate with this IDP. For the most part, this follows client configuration in node-oidc-provider.-
oidc.clients[*].client_id: The client idp for the client -
oidc.clients[*].client_secret: The client secret used in the client credentials flow -
oidc.clients[*].redirect_uris: Valid redirect uris for the client -
oidc.clients[*].allowedOrigins: Allowed origins for the client when making AJAX requests -
oidc.clients[*].token_enpoint_auth_method: The autentication method for thetokenendpoint
-
-
oidc.cookieKeys: A list of randomized strings to be used for the session cookies -
jwks: The route to the jwks generated in the previous step
-
-
redis: Configuration for the redis instance-
redis.port: Redis port -
redis.host: Redis host -
redis.prefix: A prefix that will be used for all keys stored in the redis instance
-
Step 6: Run the sever
Assuming all files are in the same folder, you can run the server by running
saml2-oidc-bridge start -c config.jsonUsing the bridge
Once the bridge is deployed and configured, OIDC-compatible applications can send requests to log in with configured SAML services. Note a few caveats:
- OIDC requests MUST use PKCE.
- The
profilescope can be provided in addition to theopenidscope if you want an ID Token with some profile information. Note that all profile information under OIDC cannot be provided as there is an insufficient overlap between OIDC and SAML. - A
providerquery parameter can be added. This will cause the saml2-oidc-bridge to skip the provider selection UI and go directly to the specified provider. The value of theproviderparam corresponds to the configuration atsaml.idps[*].name.
An example request could look like:
https://saml.dcconsortium.org/auth?
client_id=some-client-id&
redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Foidcdebugger.com%2Fdebug&
scope=openid%20profile&
response_type=code&
response_mode=form_post&
code_challenge_method=S256&
code_challenge=_UxY46vb_MnzT4OACEZS18ptTRMknEvGg2OfgT5V-IA&
state=iben3lqhdg&nonce=uxx9q08zxu&
provider=example-saml-idp
Liscense
MIT